Email
October Weed of the Month: Non-native Bush Honeysuckles in Minnesota
| From | Minnesota Department of Agriculture <[email protected]> |
| Subject | October Weed of the Month: Non-native Bush Honeysuckles in Minnesota |
| Date | October 3, 2022 4:12 PM |
Links have been removed from this email. Learn more in the FAQ.
Links have been removed from this email. Learn more in the FAQ.
Exotic honeysuckle are detrimental to our forests
department of agriculture
Having trouble viewing this email? View it as a Web page [ [link removed] ].
October 3, 2022
October Weed of the Month: Non-native Bush Honeysuckles in Minnesota
*Maggie Barnick <[email protected]> <[email protected]>,?Minnesota Department of Agriculture*
Because non-native bush honeysuckles have pretty flowers and thrive in a variety of soil conditions, they were planted as ornamentals, for erosion control purposes, and as wildlife habitat. Now we know exotic honeysuckle are detrimental to our forests, spreading and outcompeting native forest understory plant species.
________________________________________________________________________
Fruit growing on a honeysuckle [ [link removed] ]
"Fall berries on a non-native bush honeysuckle."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
Non-native honeysuckles leaf out earlier and hold their leaves later than native shrubs, shading out native plants. They also begin absorbing nutrients and water earlier in the growing season, depriving our native plants of these critical resources. In the fall, you can notice their colorful red to orange-yellow berries, which are eaten and distributed by bird species, and although they have little actual nutritional value for our native birds, this creates an important vehicle of spread into new areas. Finally, their shallow root systems leave the soils more prone to erosion.
________________________________________________________________________
Honeysuckle in flower [ [link removed] ]
""Non-native bush honeysuckle" in flower."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
There are 180 species in the "Lonicera" genus worldwide. In Minnesota, we have four non-native bush honeysuckle species of concern: Morrow?s, Bell?s, Tatarian, and Amur honeysuckles. Bell?s honeysuckle is a hybrid of Tatarian and Morrow?s honeysuckle. Morrow?s, Bell?s, and Tatarian honeysuckle are all widespread in Minnesota. Bell?s honeysuckle is thought to be the most common. Amur honeysuckle is not known to be widespread in Minnesota but exhibits similar invasive characteristics as the other three and is a problem in other parts of the Midwest. Amur honeysuckle has the most distinctive characteristics of the four species. It has leaves that are lance shaped with tapered, pointy tips. Its fruits and flowers are nearly stalkless. Non-native bush honeysuckle can be quite difficult to distinguish from one another. The four species exhibit slightly different characteristics in flower color, leaf pubescence, fruit color, and size, too. A guide to distinguishing non-native from native honeysuckles is on pages 14-15 of "Mistaken Identity? Invasive Plants and their Native Look-alikes [ [link removed] ]."
________________________________________________________________________
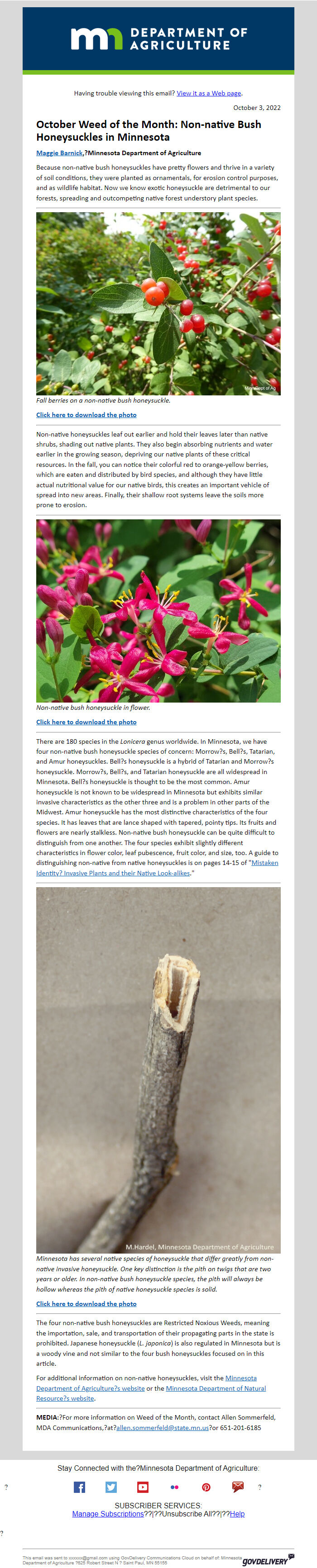
Twig of a honeysuckle [ [link removed] ]
"Minnesota has several native species of honeysuckle that differ greatly from non-native invasive honeysuckle. One key distinction is the pith on twigs that are two years or older. In non-native bush honeysuckle species, the pith will always be hollow whereas the pith of native honeysuckle species is solid."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
The four non-native bush honeysuckles are Restricted Noxious Weeds, meaning the importation, sale, and transportation of their propagating parts in the state is prohibited. Japanese honeysuckle ("L. japonica") is also regulated in Minnesota but is a woody vine and not similar to the four bush honeysuckles focused on in this article.
For additional information on non-native honeysuckles, visit the Minnesota Department of Agriculture?s website [ [link removed] ] or the Minnesota Department of Natural Resource?s website [ [link removed]). ].
________________________________________________________________________
*MEDIA:*?For more information on Weed of the Month, contact Allen Sommerfeld, MDA Communications,[email protected]?or 651-201-6185
Stay Connected with the?Minnesota Department of Agriculture: ? Facebook [ [link removed] ] Twitter [ [link removed] ] Youtube [ [link removed] ] Flickr [ [link removed] ] Flickr [ [link removed] ] Govdelivery [ [link removed] ] ?
SUBSCRIBER SERVICES:
Manage Subscriptions [ [link removed] ]??|??Unsubscribe All [ [link removed] ]??|??Help [ [link removed] ]
?
________________________________________________________________________
This email was sent to [email protected] using GovDelivery Communications Cloud on behalf of: Minnesota Department of Agriculture ?625 Robert Street N ? Saint Paul, MN 55155 GovDelivery logo [ [link removed] ]
body .abe-column-block {min-height: 5px;} table.gd_combo_table img {margin-left:7px; margin-right:7px;} table.gd_combo_table div.govd_image_display img, table.gd_combo_table td.gd_combo_image_cell img {margin-left:0px; margin-right:0px;}
department of agriculture
Having trouble viewing this email? View it as a Web page [ [link removed] ].
October 3, 2022
October Weed of the Month: Non-native Bush Honeysuckles in Minnesota
*Maggie Barnick <[email protected]> <[email protected]>,?Minnesota Department of Agriculture*
Because non-native bush honeysuckles have pretty flowers and thrive in a variety of soil conditions, they were planted as ornamentals, for erosion control purposes, and as wildlife habitat. Now we know exotic honeysuckle are detrimental to our forests, spreading and outcompeting native forest understory plant species.
________________________________________________________________________
Fruit growing on a honeysuckle [ [link removed] ]
"Fall berries on a non-native bush honeysuckle."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
Non-native honeysuckles leaf out earlier and hold their leaves later than native shrubs, shading out native plants. They also begin absorbing nutrients and water earlier in the growing season, depriving our native plants of these critical resources. In the fall, you can notice their colorful red to orange-yellow berries, which are eaten and distributed by bird species, and although they have little actual nutritional value for our native birds, this creates an important vehicle of spread into new areas. Finally, their shallow root systems leave the soils more prone to erosion.
________________________________________________________________________
Honeysuckle in flower [ [link removed] ]
""Non-native bush honeysuckle" in flower."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
There are 180 species in the "Lonicera" genus worldwide. In Minnesota, we have four non-native bush honeysuckle species of concern: Morrow?s, Bell?s, Tatarian, and Amur honeysuckles. Bell?s honeysuckle is a hybrid of Tatarian and Morrow?s honeysuckle. Morrow?s, Bell?s, and Tatarian honeysuckle are all widespread in Minnesota. Bell?s honeysuckle is thought to be the most common. Amur honeysuckle is not known to be widespread in Minnesota but exhibits similar invasive characteristics as the other three and is a problem in other parts of the Midwest. Amur honeysuckle has the most distinctive characteristics of the four species. It has leaves that are lance shaped with tapered, pointy tips. Its fruits and flowers are nearly stalkless. Non-native bush honeysuckle can be quite difficult to distinguish from one another. The four species exhibit slightly different characteristics in flower color, leaf pubescence, fruit color, and size, too. A guide to distinguishing non-native from native honeysuckles is on pages 14-15 of "Mistaken Identity? Invasive Plants and their Native Look-alikes [ [link removed] ]."
________________________________________________________________________
Twig of a honeysuckle [ [link removed] ]
"Minnesota has several native species of honeysuckle that differ greatly from non-native invasive honeysuckle. One key distinction is the pith on twigs that are two years or older. In non-native bush honeysuckle species, the pith will always be hollow whereas the pith of native honeysuckle species is solid."
*Click here to download the photo [ [link removed] ]*
________________________________________________________________________
The four non-native bush honeysuckles are Restricted Noxious Weeds, meaning the importation, sale, and transportation of their propagating parts in the state is prohibited. Japanese honeysuckle ("L. japonica") is also regulated in Minnesota but is a woody vine and not similar to the four bush honeysuckles focused on in this article.
For additional information on non-native honeysuckles, visit the Minnesota Department of Agriculture?s website [ [link removed] ] or the Minnesota Department of Natural Resource?s website [ [link removed]). ].
________________________________________________________________________
*MEDIA:*?For more information on Weed of the Month, contact Allen Sommerfeld, MDA Communications,[email protected]?or 651-201-6185
Stay Connected with the?Minnesota Department of Agriculture: ? Facebook [ [link removed] ] Twitter [ [link removed] ] Youtube [ [link removed] ] Flickr [ [link removed] ] Flickr [ [link removed] ] Govdelivery [ [link removed] ] ?
SUBSCRIBER SERVICES:
Manage Subscriptions [ [link removed] ]??|??Unsubscribe All [ [link removed] ]??|??Help [ [link removed] ]
?
________________________________________________________________________
This email was sent to [email protected] using GovDelivery Communications Cloud on behalf of: Minnesota Department of Agriculture ?625 Robert Street N ? Saint Paul, MN 55155 GovDelivery logo [ [link removed] ]
body .abe-column-block {min-height: 5px;} table.gd_combo_table img {margin-left:7px; margin-right:7px;} table.gd_combo_table div.govd_image_display img, table.gd_combo_table td.gd_combo_image_cell img {margin-left:0px; margin-right:0px;}
Message Analysis
- Sender: Minnesota Department of Agriculture
- Political Party: n/a
- Country: n/a
- State/Locality: n/a
- Office: n/a
-
Email Providers:
- govDelivery
