Biden's Afghan Shell Game Prompts Media Shrugs and Stenography
Julie Hollar

More than a year after it froze $7 billion of Afghanistan's central bank reserves in the wake of the Taliban's military victory, the US has announced it will use half the money to establish a fund at a Swiss bank to help stabilize the cratering Afghan economy.
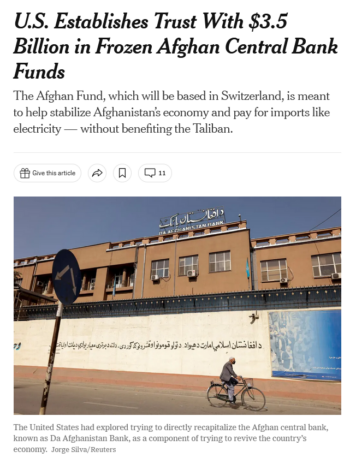 The New York Times (9/14/22) wrote that the US "explored trying to directly recapitalize the Afghan central bank"—in other words, considered giving some of Afghanistan's money back to Afghanistan.
President Joe Biden's refusal over the past year to allow the Afghan central bank access to its own reserves has caused an economic crisis that has pushed most of the population into extreme poverty and malnutrition. Moreover, in February, Biden announced that he was reserving half of Afghanistan's money for families of 9/11 victims, sparking international outrage—and yawns from TV news outlets (FAIR.org, 2/15/22).
The establishment of the "Afghan Fund" is a half measure that, while almost certain to provide some much needed relief, continues both the unjust theft of half the funds and the hobbling of the country's recovery by undermining the central bank. (Economist Andrés Arauz describes Biden's plan as "starting a parallel private foundation 'central bank' from scratch," and argues that it's a "terrible idea"—CEPR, 9/15/22.)
When a government invades a country, occupies it for 20 years, and then sends it into a humanitarian crisis by appropriating most of its money, you'd expect good journalists from that country to follow the story closely and vigorously hold their government to account. In the US, instead, you get largely shrugs and government talking points.
Obscuring US responsibility
The story of Biden's reallocation of Afghanistan's reserves wasn't mentioned by a single TV news outlet, according to a search of the Nexis news database. That failure is sadly unsurprising, given their overwhelming lack of interest in the Afghan people once the US military withdrawal was complete—after incessant wailing about the fate of those people during the withdrawal itself (FAIR.org, 12/21/21).
 The AP story the LA Times (9/15/22) ran on the Biden administration's reallocation of Afghanistan's banking reserves didn't quote any Afghans.
The Los Angeles Times (9/15/22) ran an AP report on the funds on its front page. That report—which also ran in major papers like the Chicago Tribune and Baltimore Sun—obscured the US responsibility for the situation, using passive language to explain that "international funding to Afghanistan was suspended" and "billions of dollars of the county's assets abroad, mostly in the United States, were frozen" after the US withdrawal.
That Biden had unilaterally announced that half the money would be effectively stolen from the Afghan people, who had nothing to do with 9/11, and reserved for families of 9/11 victims, was likewise reported with passive language and no hint of controversy: "The other $3.5 billion will stay in the US to finance payments from lawsuits by US victims of terrorism."
The only quotes the AP offered were from US officials and the Swiss bank.
CNN.com (9/14/22) also quoted only US officials, and offered the rather credulous assessment: “By setting up this mechanism, the US is making it clear that they intend to get the frozen funds to the Afghan people”—which is hard to square with the earmarking of fully half the funds for US citizens, not the Afghan people.
'Unusual dilemma'
 The Washington Post headline (9/14/22) reflects the framing that Afghanistan is to blame for the theft of its reserves: "US officials say the Taliban has refused to do what is necessary for the funds to be returned."
The New York Times and Washington Post at least included a human rights critic each, but still included language downplaying US culpability. At the Times (9/14/22), reporter Charlie Savage told readers the crisis is “a highly unusual dilemma”:
Afghanistan’s economy went into a free fall when its government collapsed amid the Taliban’s takeover in August 2021. Financial aid and international spending dried up, in part because the Taliban are a designated terrorist group subject to US and international sanctions that make it a crime to transfer money that could reach them.
In this framing, it's not US sanctions that are to blame, but rather the fact that the "Taliban are a designated terrorist group" and thus subject to sanctions. Designated by whom? By not answering this question, the Times deflects attention from US decision-making and its catastrophic impact on the Afghan people.
The only unalloyed criticism appearing in any US news outlet we could find came from Mark Weisbrot of the Center for Economic and Policy Research, who told the Washington Post (9/14/22), “This move can’t possibly compensate for the harm to the Afghan economy and millions of people who are starving, in large part because of the US confiscation of Afghanistan’s central bank reserves.”
The Post's Jeff Stein also was nearly alone in including criticism from a spokesperson for the Afghan central bank. (The only other major US news outlet we found that included a quote from a Taliban spokesperson was the Wall Street Journal—9/14/22).
Even so, the Post couldn't help tucking an old-fashioned both-sidesing into the story:
Economists say the freezing of these funds has fueled the collapse of Afghanistan’s economy and its hunger crisis, but the Biden administration and other analysts have said the Taliban cannot be trusted to administer such substantial amounts of money.
Urging release of funds
 The Intercept report (6/6/22) frankly refers to "the humanitarian disaster triggered by the Biden administration’s decision to seize Afghanistan’s $7 billion in banking reserves."
The US isn't alone in its concerns about the Taliban, but Washington's argument is disingenuous. Central bank funds are not the property of the country's government, and that government cannot simply withdraw them for its own purposes; the vast majority—some 90%—of the bank's holdings in fact belong to Afghan citizens and businesses (CEPR.net, 9/15/22).
That's why a wide range of individuals and groups around the world, including human rights groups, economists and the UN secretary general, have urged the release of the entirety of the funds to the central bank.
The earmarking of half the funds for 9/11 families—which a group of economists including Joseph Stiglitz called "arbitrary and unjustified"—is particularly galling. Kelly Campbell, co-founder of 9/11 Families for Peaceful Tomorrows, told the Intercept (6/6/22):
The fact of the matter is that these reserves are the Afghan people’s money. The idea that they are on the brink of famine and that we would be holding on to their money for any purpose is just wrong. The Afghan people are not responsible for 9/11, they’re victims of 9/11 the same way our families are. To take their money and watch them literally starve—I can’t think of anything more sad.
Missing: women's voices
 Al Jazeera (12/4/21): "The Afghan people should not be denied vital healthcare and be abandoned without food because the international community sees economic starvation as the only available tool to influence the Taliban regime. "
Even those the West most professes concern for, Afghan women, have deeply criticized Biden's handling of the funds. In March, the US canceled talks in Doha with the Taliban about the funds, ostensibly because the Taliban reversed its decision to allow girls to attend high school (Reuters, 3/27/22). But as Jamila Afghani, founder and president of the Afghan chapter of the Women’s International League for Peace and Freedom, pointedly argued (Al Jazeera, 12/4/21): “We are not supporting Afghan women by starving them.”
In an op-ed for Foreign Policy (1/31/22) several months into the freeze, Jamila Afghani and Yifat Susskind of the global women's human rights group MADRE argued that US policymakers' framing of the situation offers a false choice between economic relief and women's rights—which, they point out, is "grounded in historical hypocrisy," as the US used women's rights to justify their war, despite spending nearly 1,000 times more on military operations than promoting women's rights. (See FAIR.org, 8/23/21.)
"In reality," Afghani and Susskind wrote, "the best way for policymakers to ensure their actions promote an effective economic recovery is to center the voices of Afghan women leaders and heed their recommendations."
US journalists' over-reliance on official sources means that the false choice between economic relief and women's rights is not just the dominant policymaker narrative, but the dominant media narrative as well. In not a single story in the latest round of coverage was an Afghan woman's voice heard—let alone centered. Nor were any civilian male voices heard, for that matter. In a story fundamentally about the fate of the Afghan people, to US journalists, those people are little more than silent pawns.
|
