It's the Economic Reporting, Stupid
Conor Smyth

 Ask voters to verify basic facts related to major political issues, and the results are depressing. An Ipsos survey from October of this year, for instance, discovered most Americans were unaware that unauthorized border crossings were at or near their lowest point over the last several years, that violent crime was not at or near all-time highs in most major cities—and that inflation was down from a year earlier and near historic averages. Ask voters to verify basic facts related to major political issues, and the results are depressing. An Ipsos survey from October of this year, for instance, discovered most Americans were unaware that unauthorized border crossings were at or near their lowest point over the last several years, that violent crime was not at or near all-time highs in most major cities—and that inflation was down from a year earlier and near historic averages.
The political implications of such ignorance are both predictable and striking, with more ignorance associated with greater support for Donald Trump.
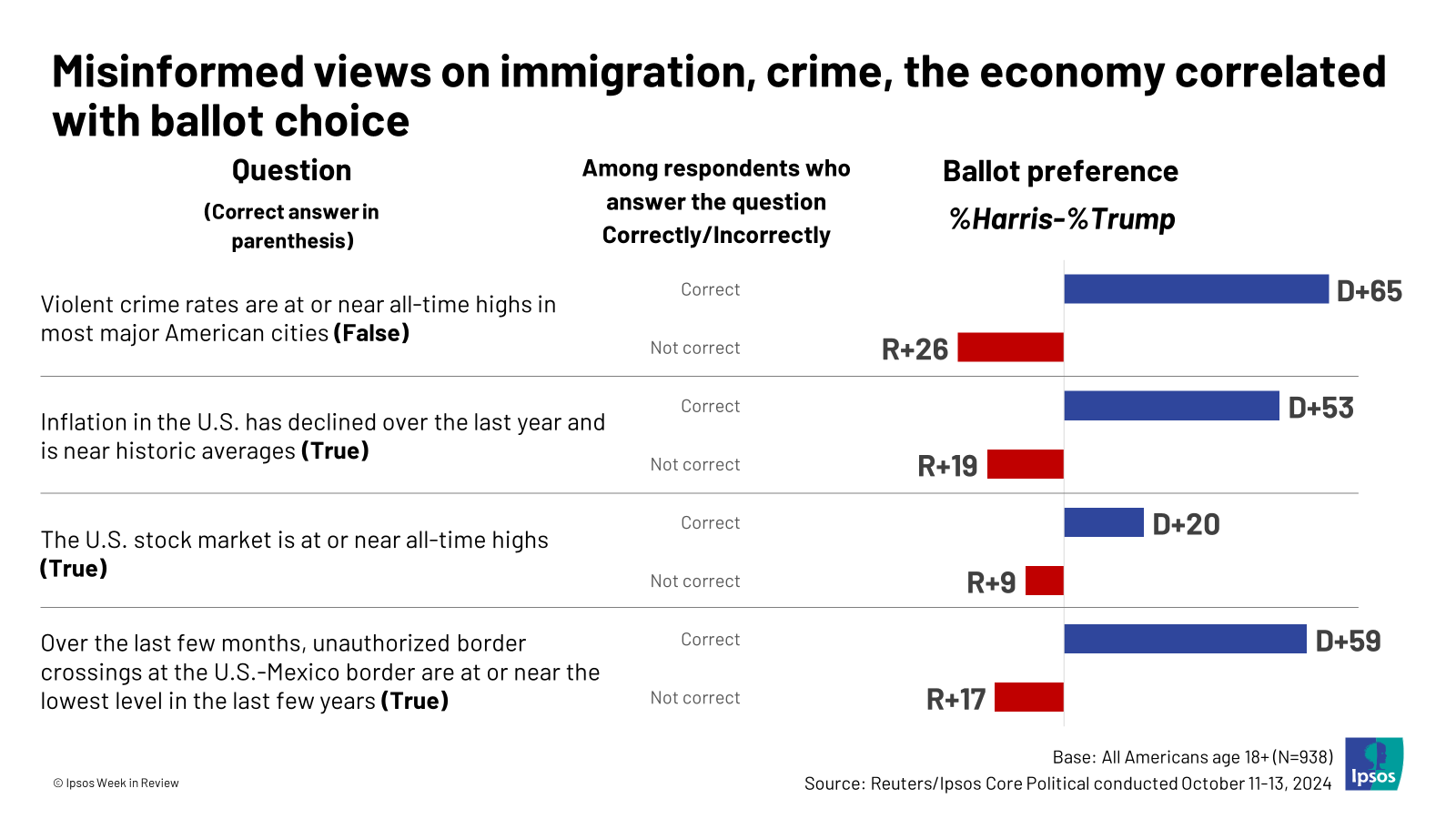
Conservative media, unsurprisingly, appears to be a major culprit in the miseducation of the American public, with people whose primary media source is conservative media registering lower familiarity with reality than those who stuck mainly to other media sources. (Reliance on social media, too, was associated with less knowledge of basic facts.)
But even among those who primarily get their news from the more general category of cable/national newspapers, a third didn’t realize that inflation had declined over the past year. Voters’ lack of knowledge, therefore, cannot simply be laid at the feet of the conservative press. Corporate outlets more broadly must share the blame.
And on perhaps no other issue has corporate media’s failure to inform been more consequential than on inflation. This was, after all, arguably the key factor in the election: Inflation surged, and Democrats were pummeled.
Did they deserve this fate, though? That’s a tougher question, but one that corporate media could help the public grapple with—if only they weren’t committed to misinforming the public about the issue at hand.
Artificially spiking Trump's economy
It would be absurd to expect the public at large to have the time or ability to do a deep dive into statistics in order to develop as accurate an image of the economy as possible. It wouldn’t be so absurd, however, to expect journalists to perform this task. After all, their essential function is to deliver high-quality, accurate information to a lay audience. Unfortunately, in reality, they often fail at this job. We might refashion an old phrase to say: There are lies, damned lies and statistics as represented by journalists.
Take a recent piece by Washington Post columnist, and former economics correspondent, Heather Long (11/8/24). In it, she makes the claim that voters enjoyed much more robust wage growth under Trump than under Joe Biden, after accounting for inflation. Her column includes a chart showing wage growth outpacing inflation by 7.6 percentage points under Trump and only 0.6 percentage points under Biden.
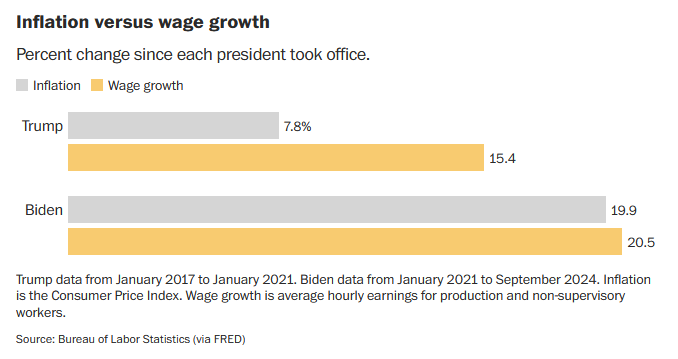
Something important goes unmentioned here, something that might surprise a casual reader. Specifically, there was a serious and well-known—at least among experts—methodological issue that led to an artificial spike during 2020/2021 in the wage measure Long is citing. As many more low-wage than high-wage workers lost their jobs at the height of the pandemic, this measure artificially inflates wage growth under Trump and deflates it under Biden. Maybe an issue worth mentioning, if you’re making a claim about comparative real wage growth under the two.
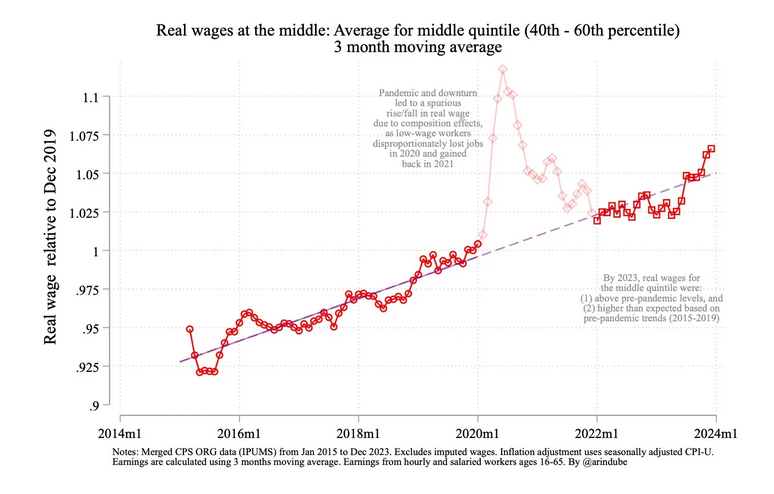
When you chart the measure the Washington Post (11/8/24) used to show the superiority of Trump's wage growth, it's revealed as an artifact of people dropping out of the workforce during the pandemic (Arin's Substack, 1/18/24).
Does Long mention this, though? No. Will the average reader be sufficiently in the economic weeds to know she is misleading them? Also no.
An unreal measure of real income

What explains everything for the Atlantic (11/11/24) is a cost-of-living crisis that disappears if you use a better measures of the cost of living.
Another offending piece appeared recently in the Atlantic (11/11/24). There, staff writer Annie Lowrey made the case that the cost-of-living crisis, and the Democrats’ inability to tackle it, explains the election results. Curiously, the media’s role in distracting the public from the remarkable achievements of macroeconomic policy during Biden’s tenure in office went unmentioned.
Lowrey at least acknowledged how impressive the macroeconomic figures have been coming out of the Covid downturn, but she asserted that this obscured a darker story: “Headline economic figures have become less and less of a useful guide to how actual families are doing.” Instead of relying solely on these numbers, Lowrey proposed consulting “more granular data” that “pointed to considerable strain.”
First among these data points was an apparent fall in real median income since 2019. As Lowrey put it, “Real median household income fell relative to its pre-Covid peak.”
What she failed to disclose was the flimsiness of the underlying measure being used. As economist Dean Baker (Beat the Press, 9/10/24) pointed out a couple months back, when the Washington Post (9/10/24) ran a piece highlighting trends in the same metric—a median income measure designed by the Census Bureau—making a comparison between the 2024 figure and the 2019 one is messy:
The problem is with the comparison to 2019, the last year before the pandemic. There was a large problem of non-response to the survey for 2019, which was fielded in the middle of the pandemic shutdown in the spring of 2020. The Census Bureau wrote about this problem when it released the 2019 data in the fall of 2020.
As a result of the non-response issue, the 2019 number is artificially inflated, and a comparison between it and more recent figures, which seem to also be inflated but to a lesser degree, is difficult at best. Other measures of income, meanwhile, find real income increasing for Americans since 2019. These critical pieces of information, however, are missing from the Lowrey piece.
Sloppy reporting of real problems
This is not to say that Lowrey and others who have made similar arguments don’t have a point that there are real issues facing the American public. For such a wealthy country, the US has obscenely high poverty, internationally aberrant levels of inequality, and a notoriously ramshackle welfare state.
Partially out of sheer necessity, the US welfare state was substantially boosted during the pandemic, and the unwinding of this enhanced safety net after 2021 must have had some effect on Americans’ perceptions of the economy and their own economic standing. Real disposable income, for example, spiked in 2021 due to temporary measures like stimulus checks, but then fell back to the pre-pandemic trend of growth, which may have felt like a loss to some.
And though the Washington Post's Long mucked up her analysis of wage trends under the Biden and Trump presidencies, the data that we have does indicate that inflation bit into workers’ wages early in Biden’s term, with median real wage growth turning negative in 2021 and 2022. (It’s nonetheless worth noting that these wage declines were concentrated among high-wage workers, not low-wage ones.)
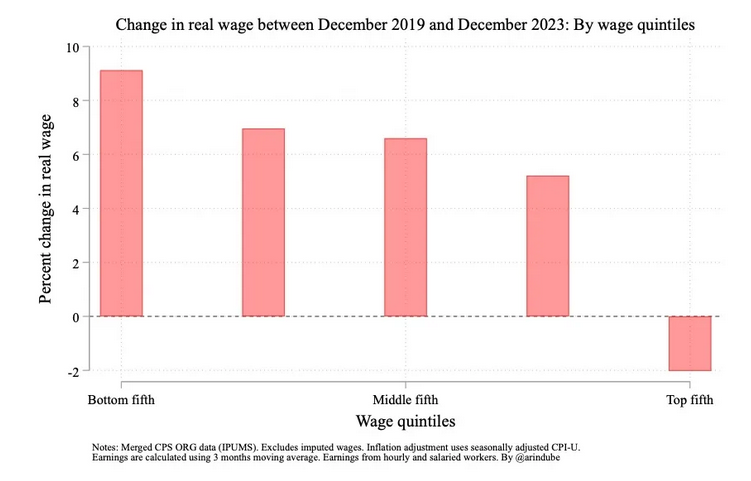
From December 2019 through December 2023, inflation-adjusted growth in wages was highest in the poorest quintile, and only negative for the top quintile (Arin's Substack, 1/18/24).
Clearly, there are reasons for people to be angry about the economy. The issue is that imprecise descriptions of the trajectory of the US economy over recent years leave people unable to decipher how the economic situation has deteriorated, and in which ways there actually has been improvement.
Citing a flawed measure of median income to suggest that people are worse off than in 2019, for example, is careless at best. We know that, even after adjusting for inflation, Americans’ wages, disposable incomes and, perhaps most crucially, spending levels are higher today than they were in 2019. Notably, this is true across income groups, with real retail spending up for low-, middle- and high-income households.
There are many ways in which the US economy flatly fails, but addressing those failures becomes even harder when the public is misled into thinking that inflation is outpacing wages, or that real median income is actually decreasing.
Joblessness affects 'only a minority'
For the New York Times (11/8/24), inflation affects "everyone," whereas unemployment matters to "only a minority of the population."
Messing up the technical details when presenting statistical information is bad enough. But corporate media misinformation goes beyond that. Recently, for instance, the New York Times (11/8/24) decided to add to the barrage of inflation misinformation by blatantly misrepresenting how inflation and unemployment affect the public. In a piece titled “How Inflation Shaped Voting,” reporter German Lopez wrote:
Why does inflation anger voters so much? Some economic problems, like high unemployment, affect only a minority of the population. But higher prices affect everyone.
This is wrong. An increase in unemployment has economy-wide effects, dragging down wage growth across the income distribution, though particularly at the bottom. In fact, the societal effects of higher unemployment seem to be much more dramatic than those of higher inflation. According to a piece from the Times (7/20/22) published back in 2022:
In a 2003 paper, the economist Justin Wolfers, then of Stanford University, found that a percentage-point increase in the unemployment rate caused roughly five times as much unhappiness as a percentage-point increase in inflation.
Had Lopez written that high unemployment directly affects a small percentage of the population, he obviously would have been on solid ground. But that’s not what he wrote.
Skewing in one direction
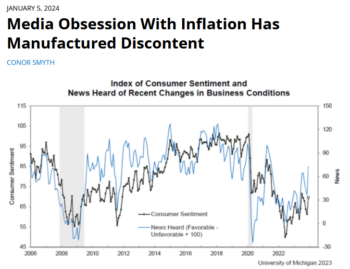
"There’s another fundamental cause of economic discontent that should be getting more attention: corporate media’s single-minded obsession with inflation, which has left the public with an objectively inaccurate view of the economy" (FAIR.org, 1/5/24).
These criticisms of how journalists present economic information are technical, but they are important. Notably, in each instance cited, the skewing of facts has specific political implications.
In Long’s piece, workers’ gains under Trump were exaggerated, and their gains under Biden were understated. In Lowrey’s piece, income gains under Biden were disregarded. And in Lopez’s piece, the negative impacts of increased unemployment, which the Biden administration avoided at the cost of a somewhat larger spike in inflation, were downplayed. The negative effects of inflation were played up.
It’s not hard to see how such an approach to reporting will benefit one political party at the expense of the other. This would be totally reasonable if the reporting were based in reality, with journalists sticking to the facts and representing statistics with care. But that’s not what’s happening.
Instead, journalists over the past several years have engaged in a collective freak-out over a surge in inflation, feeding the public’s pre-existing negativity bias with a hyper-fixation on rising prices in economic coverage. That this coverage has not only overshadowed coverage of more positive economic stories—such as the successes of a historically progressive stimulus bill, and the massive wage gains it has spurred—but has misled the public about basic economic facts in the process is a scandal.
Journalists should face flak for imprecision in their reporting, and should be pushed to improve when they fall short of a high standard of accuracy, especially when they occupy elite perches in the US media environment. Otherwise, an information environment polluted by conservative outlets and social media misinformation will never get cleaned up. If corporate media’s mission is truly to inform the public, they have a long way to go.
|
